In the ever-evolving landscape of IT, virtualized infrastructure emerges as a game-changer. This technology transforms traditional operations into dynamic, efficient systems. With virtualized infrastructure, resources are no longer confined to individual machines. Instead, they pool together, optimizing utilization and slashing hardware costs. Flexibility takes center stage, allowing quick adjustments to meet fluctuating demands. Management becomes a breeze with centralized control, ensuring seamless updates and backups. This article delves into the realm of virtualized infrastructure, revealing how it reshapes IT operations for the better.
What is Virtualized Infrastructure?
In this section, let’s dive into the world of virtualized infrastructure and its profound impact on IT operations.
Definition of virtualized infrastructure
Virtualized infrastructure, often referred to simply as virtualization, represents a fundamental shift in how businesses manage their IT resources. In this context, “virtualized” implies creating virtual, software-based representations of physical hardware components. These virtual entities include servers, storage devices, and networking equipment. They mirror the functionality of physical counterparts but exist within a shared pool of resources. This means that instead of dedicating separate physical machines for different tasks, virtualized infrastructure allows multiple virtual instances to run on a single physical server.
These virtual instances run independently, enabling businesses to efficiently allocate resources based on demand. Virtualization technology abstracts the underlying hardware details, providing a layer of separation between the physical components and the virtual ones. By doing so, it minimizes the need for extensive hardware investments and provides an environment where resources can be efficiently utilized.
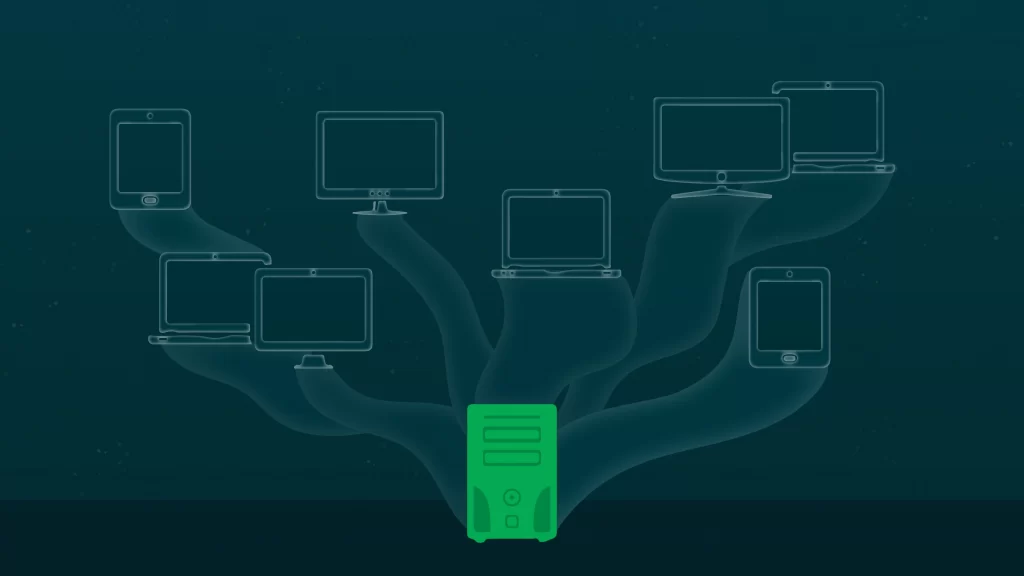
This transformative approach has several key advantages. It reduces the number of physical servers needed, which in turn cuts down on energy consumption, space requirements, and overall hardware costs. Additionally, it offers greater flexibility and scalability, enabling businesses to scale resources up or down as needed. As we delve deeper into the article, we’ll explore how this shift to virtualized infrastructure revolutionizes IT operations, leading to enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and more agile business strategies.
Importance of virtualized infrastructure in modern IT
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern IT, virtualized infrastructure has emerged as a cornerstone of transformation. As businesses strive to become more agile, efficient, and cost-effective, traditional IT models fall short in meeting these demands. This is where virtualized infrastructure steps in. It introduces a level of flexibility and resource optimization that is unparalleled in conventional setups.
Gone are the days when each application required its dedicated hardware, leading to a sprawling and often underutilized infrastructure. Virtualized infrastructure flips this script by allowing multiple virtual instances to run on a single physical machine. This consolidation not only saves space but significantly reduces operational expenses associated with maintenance, cooling, and power consumption.
Moreover, virtualized infrastructure fuels innovation by accelerating deployment times. In the past, setting up new servers or testing environments was a time-consuming process. With virtualization, creating and deploying virtual instances takes minutes rather than hours or days. This agility empowers businesses to respond rapidly to market changes and launch new initiatives without the shackles of hardware limitations.
As digitalization reshapes industries, the importance of virtualized infrastructure becomes more pronounced. It lays the foundation for cloud computing, DevOps practices, and advanced data analytics. This article will delve further into the transformative power of virtualized infrastructure, showcasing how it redefines IT operations and positions businesses for success in the digital age.
Recommended reading: How Desktop Virtualization Revolutionizes Work
5 Advantages of Virtualized Infrastructure
Virtualized infrastructure brings a host of advantages that revolutionize the way businesses approach IT operations. By harnessing the power of virtualization, organizations can optimize resource utilization, enhance scalability, and streamline management processes. In this section, we will explore five key advantages that make virtualized infrastructure a game-changer in the realm of IT.
Enhanced Resource Utilization
One of the standout advantages of virtualized infrastructure is its ability to optimize resource utilization. In a traditional IT setup, physical servers often operate at less than full capacity, leading to inefficiencies and wastage. Virtualization changes this dynamic by pooling computing resources, including processing power, memory, and storage, into a shared environment.
This pooling allows virtual machines (VMs) to draw from the available resources as needed. If one VM requires more resources while others are idle, the surplus is reallocated on-the-fly. This ensures that computing power is allocated efficiently, eliminating the problem of “resource silos” associated with dedicated physical servers.
The result is a significant reduction in hardware costs, as fewer physical machines are required to support the same workload. Moreover, energy consumption drops considerably, since fewer servers need to be powered and cooled. This not only benefits the bottom line but also contributes to environmentally-friendly practices.
By harnessing the potential of virtualized infrastructure, organizations can achieve an unprecedented level of resource optimization. IT operations become leaner, more agile, and environmentally responsible, setting the stage for a new era of efficiency in the digital age.
Improved Scalability and Flexibility
Virtualized infrastructure introduces a new level of scalability and flexibility to IT operations, revolutionizing the way organizations manage their resources. Unlike traditional setups where adding capacity often involves purchasing and configuring new hardware, virtualization simplifies the process.
Scaling up or down becomes a seamless endeavor. As demand fluctuates, businesses can create new virtual instances or adjust the resources allocated to existing ones. This dynamic flexibility ensures that IT environments can swiftly adapt to changing needs, preventing over-provisioning and underutilization.
In the past, hardware limitations could hinder growth, forcing businesses to predict future needs and invest in advance. With virtualized infrastructure, this constraint is virtually eliminated. Organizations can allocate resources as required, ensuring a more efficient utilization of their investments.
Furthermore, this scalability extends beyond computing resources. Virtualized infrastructure is a foundational element of cloud computing, enabling businesses to expand their capabilities without being confined to the limits of physical hardware. Whether it’s scaling applications, services, or storage, virtualization provides the framework for growth in a digital landscape that demands agility and adaptability.
Streamlined Management and Maintenance
Virtualized infrastructure not only optimizes resource usage but also simplifies the way IT environments are managed and maintained. In traditional setups, managing numerous physical servers and components could be time-consuming and error-prone. Virtualization addresses this challenge by introducing a centralized approach to management.
A central management console provides a comprehensive view of the entire virtualized infrastructure. IT administrators can monitor performance, allocate resources, and apply updates from a single interface. This consolidation of control not only saves time but also enhances security, as potential vulnerabilities can be addressed swiftly across the environment.
When it comes to maintenance, virtualized infrastructure streamlines the process. Traditional updates or patches often required individual attention for each physical machine, leading to downtime and disruptions. With virtualization, updates can be applied to multiple virtual instances simultaneously, minimizing disruptions and improving uptime.
Moreover, the ability to create snapshots and backups of entire virtual machines simplifies disaster recovery. In case of data corruption or hardware failure, virtualized environments can be restored to a previous state quickly and efficiently, reducing the impact of potential downtime.
In essence, streamlined management and maintenance are integral advantages of virtualized infrastructure, allowing IT teams to work more efficiently, reduce risks, and ensure the seamless operation of critical business systems.
Enhanced Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Virtualized infrastructure offers a robust framework for enhancing disaster recovery and ensuring business continuity. In a traditional IT setup, recovering from hardware failures or data loss could be a lengthy and challenging process. Virtualization changes this narrative by introducing features that simplify and expedite recovery efforts.

Snapshots and backups are key components of virtualized disaster recovery strategies. Organizations can take snapshots of entire virtual machines at specific points in time. These snapshots serve as reliable recovery points, enabling businesses to roll back to a known working state in case of errors or system failures.
Moreover, the virtualized environment’s agility plays a significant role in business continuity. When a physical server fails, the virtual instances running on it can be rapidly migrated to other available servers. This migration can occur with minimal downtime, ensuring that critical systems remain operational.
The result is reduced downtime, which translates to minimal disruption of business operations. Virtualized infrastructure’s inherent ability to restore systems swiftly and reliably enhances an organization’s resilience against unforeseen events.
In essence, virtualized infrastructure goes beyond resource optimization. It becomes a strategic asset in disaster recovery and business continuity planning. It empowers businesses to handle disruptions effectively, recover quickly, and ensure the uninterrupted delivery of services to customers and clients.
Cost Savings and ROI
Virtualized infrastructure brings significant cost-saving opportunities, making it a compelling investment for businesses seeking to optimize their IT operations. Traditional IT models often involve substantial hardware expenses, as each application or service requires its own dedicated server. Virtualization disrupts this practice by consolidating workloads onto fewer physical machines.
The reduction in the number of physical servers directly translates to lowered capital expenditures. Businesses can achieve the same computing power with fewer machines, resulting in a smaller initial investment. Additionally, the diminished need for hardware leads to lower energy consumption and reduced cooling requirements, resulting in ongoing operational cost savings.
Moreover, virtualized infrastructure streamlines management and maintenance, further reducing operational expenses. Centralized control and automated updates minimize the need for extensive manual intervention, saving time and effort. These efficiencies contribute to a more efficient use of resources and manpower.
The return on investment (ROI) with virtualized infrastructure is substantial. Businesses not only save on hardware and operational costs but also benefit from improved agility, scalability, and reduced downtime. This translates to enhanced productivity, competitive advantage, and the ability to respond swiftly to market changes.
Recommended reading: 5 Essential Tools for Simplifying Cloud Infrastructure Management
Challenges and Considerations
While virtualized infrastructure offers remarkable advantages, it’s essential to recognize that this transformative technology comes with its share of challenges and considerations. As organizations transition to virtualized environments, they must address various factors to ensure a successful implementation and ongoing operation.
Virtualization security concerns
Amid the benefits of virtualized infrastructure, security emerges as a critical consideration. As organizations consolidate multiple virtual instances onto fewer physical servers, the attack surface can potentially expand. This scenario necessitates heightened vigilance to safeguard against potential vulnerabilities.
One key concern is “VM escape,” where an attacker gains access to the underlying hypervisor from a compromised virtual machine. This can potentially compromise the security of other VMs and the entire infrastructure. Organizations must implement robust access controls and regular security updates to mitigate this risk.
The shared nature of resources in virtualized environments can lead to concerns over data leakage between virtual machines. Effective network segmentation, strong encryption, and intrusion detection systems are vital to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Furthermore, virtualization adds complexity to security management. Traditional security solutions might not be fully compatible with virtualized environments. To address this, businesses must invest in security solutions specifically designed for virtualized infrastructure.
Ensuring adequate performance and resource allocation
While virtualized infrastructure offers numerous benefits, maintaining optimal performance and resource allocation is a challenge that organizations must address. The shared nature of resources in virtual environments can potentially lead to performance bottlenecks if not managed effectively.
Resource contention occurs when multiple virtual machines compete for the same resources. This can result in reduced performance for critical applications. Organizations must implement performance monitoring and resource allocation policies to ensure that each virtual machine receives the necessary computing power, memory, and storage.

Additionally, overprovisioning is a concern that can impact both performance and cost-effectiveness. Allocating more resources than needed to virtual machines can lead to wastage and hinder the potential benefits of virtualized infrastructure. Balancing resource allocation to match actual usage is essential.
To tackle these challenges, capacity planning becomes vital. Organizations need to understand their workloads, growth projections, and peak usage patterns. This information enables them to allocate resources judiciously and prevent potential performance issues.
Future Trends in Virtualized Infrastructure
As virtualized infrastructure continues to redefine IT operations, it’s crucial to look ahead at the evolving landscape. Experts predict several key trends that will shape the future of virtualized infrastructure, cementing its role as a transformative force within the IT domain.
1. Multicloud Strategies and Cloud Growth: The future of virtualized infrastructure is intertwined with the rise of multicloud solutions. Organizations are expected to adopt a diverse range of cloud services, spanning public clouds, private clouds, and edge locations. This multicloud approach enhances flexibility and resilience, allowing businesses to select the best-fit environment for each workload.
2. Distributed DevOps and Cloud-Native Development: DevOps practices, integral to modern software development, will extend into the realm of virtualized infrastructure. Distributed DevOps models will emerge, catering to multicloud architectures. Cloud-native development practices will become the norm, further optimizing the utilization of virtualized resources.
3. Edge Technologies and AI Integration: The proliferation of edge technologies and the integration of AI and machine learning will drive innovation in virtualized infrastructure. Edge computing, powered by virtualized environments, will enable faster data processing and real-time insights at the edge locations, enhancing responsiveness and user experiences.
4. Reshaping of IT Architectures: The future envisions a reshaped IT architecture that embraces virtualized infrastructure as a core element. This evolution will be driven by a combination of factors, including the continued growth of cloud adoption, AI-driven insights, and the need for agility in a dynamic market landscape.
As Forbes highlights, 2023 and beyond will witness a seismic shift in IT practices, influenced by multicloud strategies, edge technologies, AI integration, and cloud-native development. Organizations that embrace these trends and strategically align them with virtualized infrastructure will be well-positioned to thrive in the digital era, where adaptability and innovation are paramount.
FURTHER READING: |
1.Virtual Machine Host 101: Everything You Need to Know |
2.How to Choose a Web Hosting Provider That Meets Your Needs |
3. Understanding Risks and Solutions for Virtualization Security |
Leverage 1Byte’s strong cloud computing expertise to boost your business in a big way
1Byte provides complete domain registration services that include dedicated support staff, educated customer care, reasonable costs, as well as a domain price search tool.
Elevate your online security with 1Byte's SSL Service. Unparalleled protection, seamless integration, and peace of mind for your digital journey.
No matter the cloud server package you pick, you can rely on 1Byte for dependability, privacy, security, and a stress-free experience that is essential for successful businesses.
Choosing us as your shared hosting provider allows you to get excellent value for your money while enjoying the same level of quality and functionality as more expensive options.
Through highly flexible programs, 1Byte's cutting-edge cloud hosting gives great solutions to small and medium-sized businesses faster, more securely, and at reduced costs.
Stay ahead of the competition with 1Byte's innovative WordPress hosting services. Our feature-rich plans and unmatched reliability ensure your website stands out and delivers an unforgettable user experience.
As an official AWS Partner, one of our primary responsibilities is to assist businesses in modernizing their operations and make the most of their journeys to the cloud with AWS.
Conclusion
From enhanced resource utilization to improved scalability, the benefits of virtualized infrastructure are compelling. The advantages extend to streamlined management, robust disaster recovery, and significant cost savings. However, as with any innovation, challenges and considerations accompany the journey. Addressing security concerns, ensuring optimal performance, and navigating future trends are integral aspects that require thoughtful strategies.
As businesses set their sights on the future, the potential of virtualized infrastructure becomes even more pronounced. Multicloud strategies, AI integration, and distributed DevOps are trends that promise to redefine IT architectures. The foundation laid by virtualization positions organizations to embrace these shifts with confidence, facilitating adaptability and innovation.

