Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure Explained: A Comprehensive Guide

In the world of modern technology, “hybrid cloud infrastructure” is a term you’ve likely encountered. But what exactly does it mean? This comprehensive guide from 1Byte aims to demystify this concept, explaining it in straightforward terms. Whether you’re an IT professional or just someone curious about cloud technology, understanding hybrid cloud infrastructure is essential. Let’s delve into this guide to unravel the power and potential of hybrid cloud systems.
What is Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure?
So, what exactly is “hybrid cloud infrastructure”? It’s not as complex as it may sound. In simple terms, a hybrid cloud infrastructure combines two different types of cloud computing – public and private – to create a single, versatile system. This allows businesses to efficiently manage their data and applications. To grasp this concept fully, let’s explore the key components that make up a hybrid cloud infrastructure and see how they work together seamlessly.
Definition and Basics
In the realm of cloud computing, understanding the “hybrid cloud infrastructure” begins with its core definition and basics. This term refers to an amalgamation of two distinct cloud environments: the public cloud and the private cloud.
The public cloud is a vast, shared network of servers and resources that are maintained by third-party providers. It offers scalability and accessibility on a pay-as-you-go basis, making it an ideal choice for various applications and data.
On the other hand, the private cloud operates within a secure, dedicated environment, typically managed by the organization itself. This level of control enhances security and compliance, which is crucial for sensitive or regulated data.
What makes “hybrid cloud infrastructure” special is its ability to blend these two cloud types. This allows businesses to enjoy the best of both worlds – the cost-effectiveness and scalability of the public cloud along with the security and control of the private cloud.
In practical terms, this means that a company can store its sensitive customer data on a private cloud while utilizing the public cloud for non-sensitive tasks like web hosting. It’s a flexible approach that adapts to an organization’s specific needs. And as we delve deeper into this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover how these elements integrate seamlessly to create a powerful and adaptable cloud solution.
Key Components of Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
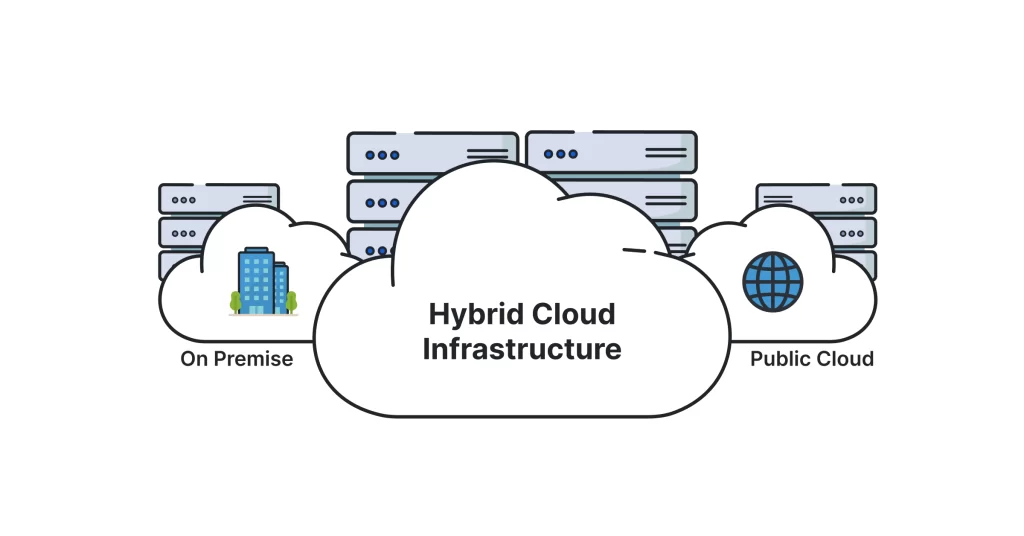
Now that we understand the basic concept of hybrid cloud infrastructure, let’s explore its key components, which are essential to comprehending how it functions.
- Public Cloud Segment: This is one of the pivotal components. It consists of cloud resources and services offered by third-party providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. These providers ensure that resources are scalable and readily available.
- Private Cloud Segment: The private cloud is another crucial piece of the puzzle. It encompasses the dedicated cloud resources maintained within an organization’s own data center. This segment provides the heightened security and control needed for sensitive data and applications.
- Connectivity: An efficient and secure connection is vital for a hybrid cloud infrastructure. This connectivity ensures that data and applications can seamlessly move between the public and private segments. It’s akin to the bridge that links these two worlds.
- Management and Orchestration: Managing a hybrid cloud infrastructure requires specialized tools and platforms that enable administrators to oversee and coordinate activities across both cloud segments. Orchestration tools automate processes and streamline management tasks.
- Security Measures: Security is paramount in a hybrid cloud setup. Robust security measures are put in place to safeguard data, applications, and communications, whether they reside in the public or private cloud segment. Encryption, access controls, and compliance protocols play a crucial role here.
- Scalability: The ability to scale resources up or down according to demand is a fundamental feature. Scalability ensures that an organization can allocate resources dynamically, optimizing costs and performance.
These key components work together harmoniously to create a hybrid cloud infrastructure. As we delve further into this comprehensive guide, you’ll see how these components collaborate to provide a flexible and efficient cloud solution that meets various business needs.
Examples of Organizations Benefiting from Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
Numerous organizations have harnessed the potential of hybrid cloud infrastructure to enhance their operations. Here are some prime examples:
- Netflix, Hulu, Uber, and Airbnb: These entertainment and travel giants make extensive use of hybrid cloud data storage. They value its on-demand and pay-per-use characteristics. For instance, when a highly-anticipated series debuts on Netflix or Hulu, their bandwidth demands surge. Similarly, Uber and Airbnb must efficiently scale their data capabilities during peak travel times, such as rush hour and holidays.
- Ensono: Ensono specializes in installing hybrid cloud environments within enterprise IT systems. This company provides solutions for managing public cloud services like AWS and Azure while ensuring the security of private servers running mission-critical applications. Well-known brands like Sonoco, Travelodge, the State of Kansas, and the Guinness Book of World Records benefit from Ensono’s hybrid cloud expertise.
- Threat Stack: As a cloud infrastructure company, Threat Stack aids hybrid clouds in detecting security threats through real-time alerting platforms. The platform continuously analyzes cloud data to identify potentially malicious anomalies.
- IBM (Turbonomic): A subsidiary of IBM, Turbonomic employs artificial intelligence to optimize workload automation for the hybrid cloud. This AI-driven approach enhances performance, compliance, and resource usage in real-time.
These real-world examples illustrate how hybrid cloud infrastructure’s flexibility, security, and cost efficiency have become valuable assets for organizations across various industries. By adopting this approach, these companies have effectively adapted to dynamic market demands and achieved greater operational efficiency.
4 Advantages of Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
Now that we’ve established what hybrid cloud infrastructure is and its key components, it’s time to explore the advantages that make it such a compelling choice for businesses. In this section, we will delve into four distinct advantages of hybrid cloud infrastructure. These benefits shed light on why more and more organizations are embracing this versatile cloud computing approach. From scalability to cost efficiency, hybrid cloud infrastructure offers a multitude of advantages that can transform the way businesses operate. Let’s explore these benefits in detail to gain a comprehensive understanding of the value it brings.
Scalability and Flexibility

One of the primary advantages of hybrid cloud infrastructure is its scalability and flexibility.
Businesses often face fluctuating demands, with resource needs varying at different times. Hybrid cloud infrastructure caters to this by allowing organizations to scale their resources up or down as required. When faced with increased workloads or seasonal peaks, they can seamlessly tap into the public cloud segment for additional computing power and storage.
This scalability ensures that a company’s operations remain smooth, even during times of high demand. Conversely, when the demand subsides, resources can be scaled down, saving costs. This flexibility empowers businesses to adapt to changing circumstances efficiently.
In essence, hybrid cloud infrastructure serves as an elastic solution that provides the perfect balance between resource availability and cost-effectiveness. By seamlessly combining public and private cloud resources, it ensures that an organization is always ready to meet the challenges of an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency is another significant advantage of hybrid cloud infrastructure.
In a business world driven by budgets and financial prudence, cost-effective solutions are highly sought after. Hybrid cloud infrastructure offers an optimal balance between control and expense. Organizations can allocate their critical data and applications to the private cloud, ensuring a secure environment while avoiding unnecessary costs.
On the other hand, they can leverage the public cloud for less-sensitive tasks, paying only for the resources they use. This pay-as-you-go model eliminates the need for extensive upfront investments in hardware and software.
Moreover, the scalability mentioned earlier plays a role in cost efficiency. When a company can seamlessly adjust its resources to match demand, it prevents overprovisioning, where excess resources remain unused. This not only saves money but also contributes to a greener, more sustainable approach to computing.
Redundancy and Disaster Recovery
Redundancy and disaster recovery are vital aspects of hybrid cloud infrastructure.
In the event of unexpected outages or data loss, organizations must have a reliable backup plan. Hybrid cloud infrastructure excels in this area by providing redundancy. It stores critical data and applications in both the private and public cloud segments. If one segment encounters an issue, the other can seamlessly take over, ensuring continuous operations.
Moreover, disaster recovery is streamlined with hybrid cloud infrastructure. Organizations can create backup copies of their data and applications, storing them securely in the cloud. In the event of a disaster, whether natural or technological, these backups can be swiftly accessed and restored.
This approach minimizes downtime, prevents data loss, and ensures business continuity. It’s an invaluable advantage, particularly for businesses that rely heavily on data and require uninterrupted operations. Hybrid cloud infrastructure offers peace of mind by providing a robust safety net to protect against unexpected disruptions.
Compliance and Security
Compliance and security represent another key advantage of hybrid cloud infrastructure.
In today’s data-driven world, ensuring the security and compliance of sensitive information is paramount. Hybrid cloud infrastructure accommodates this need by allowing organizations to allocate their most critical and regulated data to the private cloud segment. This controlled environment, managed within the organization’s own data center, provides the highest level of security and compliance.
Concurrently, the public cloud segment offers a secure and well-regulated environment, thanks to the robust security measures of leading cloud providers. This is suitable for less-sensitive data and applications.
Furthermore, hybrid cloud infrastructure facilitates data encryption and access controls, enhancing security. It provides the flexibility for organizations to tailor their security and compliance measures to meet specific industry or regulatory requirements.
By merging these two cloud segments, organizations can maintain the highest standards of security and compliance for their sensitive data while harnessing the cost-effective and scalable advantages of the public cloud. This balance between security and flexibility is a compelling reason why many businesses opt for hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Challenges and Considerations
As we uncover the potential of hybrid cloud infrastructure, it’s essential to acknowledge that it’s not without its challenges and considerations. This section will delve into the various factors that organizations must bear in mind when implementing and managing a hybrid cloud solution. While the advantages are abundant, addressing these challenges proactively is crucial to realizing the full potential of this technology. From integration hurdles to security concerns, understanding these aspects is vital to navigate the hybrid cloud landscape effectively. Let’s explore the key challenges and considerations associated with hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Integration Challenges

Integration challenges are a common consideration in the world of hybrid cloud infrastructure.
When an organization decides to adopt a hybrid cloud approach, they often need to integrate their existing on-premises systems with the cloud-based infrastructure seamlessly. This is where integration challenges may arise. It’s imperative to ensure that all systems, whether in the private or public cloud, work together harmoniously.
Integration involves connecting various software, applications, and data sources, and it can be complex. Legacy systems may not readily support cloud integration, requiring additional development and investment. Additionally, maintaining data consistency and accessibility across different environments is a crucial consideration.
Moreover, the organization must establish efficient data transfer mechanisms between the two cloud segments. This involves addressing issues like data migration, data synchronization, and ensuring that the data remains available during the transition.
Effective planning and robust integration strategies are vital to overcome these challenges. Addressing these concerns is essential for reaping the benefits of hybrid cloud infrastructure while ensuring that the organization’s operations continue to run smoothly.
Data Management and Governance
Data management and governance are vital considerations in the realm of hybrid cloud infrastructure.
When an organization operates across multiple cloud environments, ensuring consistent and effective data management is a critical challenge. Data may be spread across private and public clouds, which makes it imperative to maintain data integrity, security, and accessibility.
Data governance involves establishing policies and practices for data management, ensuring that data remains accurate, compliant with regulations, and secure. Achieving this consistency across hybrid cloud environments is no small feat.
Data may need to be moved between clouds, which raises concerns about data migration and synchronization. This process must be executed efficiently to prevent data loss and maintain data availability.
Additionally, ensuring that data remains secure and compliant with industry and regulatory standards is an ongoing task. It necessitates robust encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring.
Effective data management and governance strategies are essential to overcome these challenges and ensure that the organization’s data remains a valuable asset rather than a liability. In a world where data is king, this consideration is paramount when embracing hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Vendor Lock-In
Vendor lock-in is a significant consideration when it comes to hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Hybrid cloud solutions often involve using services and technologies provided by various cloud vendors, each with their unique systems and proprietary technologies. While this diversity can offer flexibility, it also introduces the risk of vendor lock-in.
Vendor lock-in occurs when an organization becomes heavily dependent on a specific cloud provider’s tools, services, or technologies. This dependency can make it challenging to migrate to another provider or make changes to the existing cloud setup.
The potential consequences of vendor lock-in include limited flexibility, increased costs, and reduced negotiating power. It’s crucial for organizations to consider this issue when designing their hybrid cloud strategy. They should aim to minimize dependence on any single vendor and ensure that data and applications are designed in a way that allows for portability between cloud environments.
By carefully managing vendor relationships and choosing technologies that are more open and interoperable, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with vendor lock-in and maintain the flexibility that hybrid cloud infrastructure promises.
Security Concerns
Security concerns are paramount in the context of hybrid cloud infrastructure.
When an organization extends its IT environment to include public and private cloud segments, it inherently broadens the attack surface for potential security breaches. The complexity of managing security across multiple cloud platforms adds an extra layer of challenge.
One concern is data security. Sensitive data, whether in the private or public cloud, must be protected from unauthorized access or breaches. This involves robust encryption and access controls, as well as continuous monitoring for suspicious activities.
Another concern relates to compliance. Organizations must ensure that their hybrid cloud setup adheres to industry and regulatory standards. Failure to meet these standards can result in legal and financial consequences.
Additionally, securing the connections and data transfers between the private and public cloud segments is essential. Data in transit is vulnerable to interception, so strong encryption and secure communication protocols are crucial.
To address these concerns, organizations must implement a comprehensive security strategy that covers all aspects of their hybrid cloud infrastructure. This includes evaluating the security measures of their cloud providers, creating robust security policies, and regularly assessing and updating their security posture. With the right approach, organizations can enjoy the benefits of hybrid cloud infrastructure while safeguarding their data and operations.
How to Implement Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
Implementing hybrid cloud infrastructure is a significant step for any organization seeking to harness the power of this versatile computing solution. In this section, we will explore the essential steps and best practices to guide you through the process. Whether you’re considering adopting hybrid cloud or in the midst of planning its implementation, understanding the key principles and steps is crucial. From assessing your needs to ensuring a smooth migration, this guide will provide insights into how to implement hybrid cloud infrastructure effectively. Let’s get started on this journey to unlocking the potential of hybrid cloud technology.
Steps to Implementing Hybrid Cloud

When implementing hybrid cloud infrastructure, it’s crucial to follow a structured approach to ensure success. Here are the key steps to guide you through the process:
- Identify Your Goals: Before diving into implementation, clearly define your objectives. What are you trying to achieve with hybrid cloud? Establish specific key performance indicators (KPIs) and criteria for success to measure your progress.
- Get Educated: Understand the technologies that underpin hybrid clouds, such as containers, Kubernetes, common operating systems, runtime environments, flexible storage, and universal developer frameworks. This knowledge will be instrumental in making informed decisions during implementation.
- Build Your Strategy: Create a comprehensive strategy for your cloud implementation. Follow a proven approach that covers discovery, design, build, proof of concept, testing, and migration. A detailed checklist ensures that no crucial aspect is overlooked.
- Brace for Impact: Implementing hybrid cloud can impact various aspects of your organization, including workflows, automation, and management policies. Collaborate closely with your company’s operations team from the outset and engage them throughout the implementation. Their involvement is critical for a successful transition.
These steps provide a solid framework for implementing hybrid cloud infrastructure effectively. By following this structured approach, you can navigate the complexities of hybrid cloud adoption while maximizing the benefits it offers to your organization.
Best Practices for a Successful Implementation
To ensure a successful implementation of hybrid cloud infrastructure, consider the following best practices:
- Choose a Consistent Architecture: Standardizing your architecture with a common operating environment is key. This consistency simplifies the transition to the cloud and allows your business to continue running on its existing foundation.
- Decide on an Orchestration Strategy: Orchestration is the glue that connects tasks across your infrastructure, creating cohesive workflows regardless of where they run.
- Simplify Monitoring and Management: Streamline your operations by implementing a single management solution that works seamlessly across your infrastructure and application suite, ensuring the smooth operation of all systems.
- Adhere to Policy and Governance: Ensure compliance with IT policies, including legal requirements, business practices, and regulatory standards.
By adhering to these best practices, you can effectively implement hybrid cloud infrastructure, optimizing its benefits while minimizing complexities and potential issues. These strategies provide a solid foundation for a successful transition to a hybrid cloud environment.
Conclusion
As you can see, hybrid cloud infrastructure is a dynamic and versatile solution that offers organizations a strategic way to meet their computing needs. This comprehensive guide has provided a clear understanding of what hybrid cloud infrastructure is, its key components, advantages, challenges, and best practices for implementation.
These days, businesses must adapt to remain competitive. Hybrid cloud infrastructure presents an opportunity to balance the benefits of public and private clouds while addressing the unique requirements of your organization. By identifying your goals, educating yourself, and following a structured approach, you can harness the power of hybrid cloud technology.
Remember, the success of a hybrid cloud implementation hinges on careful planning, integration, and a commitment to best practices. Whether you’re a small business looking to scale efficiently or a large enterprise seeking to enhance flexibility and security, hybrid cloud infrastructure is a viable option.
By staying informed, adhering to best practices, and maintaining a clear strategic vision, organizations can embark on a successful journey into the world of hybrid cloud infrastructure, unlocking its potential to transform the way they operate in the digital age.
